Smart City - Blog - LoRa vs. Zigbee: A Thorough Comparison of IoT Connectivity Technologies
26.03.2024
 1826
1826

LoRa vs. Zigbee: A Thorough Comparison of IoT Connectivity Technologies

In the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT) industry, two noteworthy technologies stand out when considering IoT network options: LoRa and Zigbee. These wireless protocols are tailored to address distinct challenges within the IoT landscape, showcasing notable differences in their features and capabilities. For those looking to make an informed IoT technology assessment, this article delves into the contrasting aspects of LoRa and Zigbee technologies, shedding light on their strengths and the types of projects for which they are ideally suited.
LoRa (Long Range) stands as a proprietary wireless technology created by Semtech. Functioning within unlicensed frequency bands spanning the sub-GHz range of 400–900 MHz, this technology is specifically engineered for energy-efficient communication among devices within IoT networks.
Utilizing CHIRP modulation, LoRa achieves remarkable range and signal penetration capabilities, making it well-suited for wireless IoT communication across extensive distances. In terms of use case suitability, examples include smart cities, remote resource metering, smart agriculture, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking.
Zigbee, an open standard developed by the Zigbee Alliance (a consortium of diverse companies across various industries) functions within the 2.4 GHz frequency band, employing mesh topology. This design facilitates direct communication between devices or through intermediary nodes, establishing a dependable and scalable network.
With its focus on low signal latency and high device density, Zigbee finds its niche in applications like home automation, smart lighting, and industrial control systems.
Both technologies share the common goal of linking devices within IoT networks, yet they diverge in technical features, leading to distinctly different applications. Every project of course has different device requirements and these communication protocols vary in terms of their range, operating frequency, coverage, device power consumption, data transfer speed, and data throughput.
Let’s explore the differences between LoRa and Zigbee technologies in greater detail.
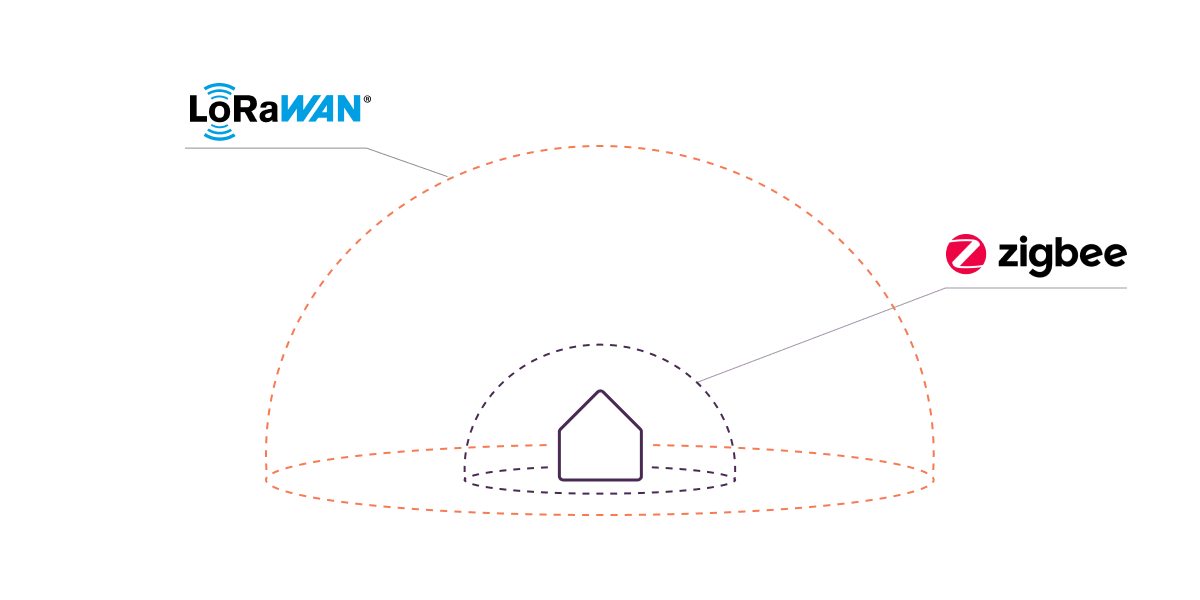
LoRa boasts a notably extended range. In urban settings, sensors within a LoRa network can establish communication over distances of up to 3.1 miles, while in open areas, this range expands to 9.3 miles. This positions LoRa as the favored option for solutions covering vast areas or requiring connectivity in remote locales.
For range comparison, devices operating within a Zigbee network transmit information over comparatively shorter distances, reaching up to 328 feet. Consequently, Zigbee networks find frequent application in confined spaces such as a single home, building, enterprise, or institution.
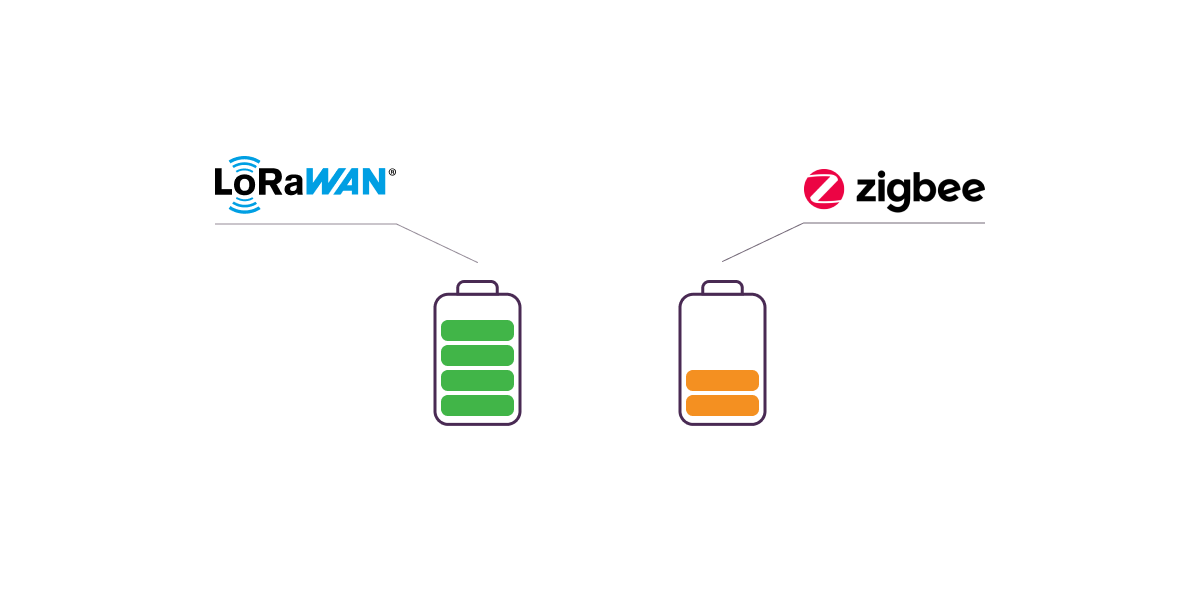
LoRa offers low power consumption as a key feature, enabling devices within the network to function on battery power for extended durations without frequent replacements. For instance, the autonomous power supply in LoRa devices extends up to an impressive 10 years.
While sensors in Zigbee networks also ensure low power consumption, in systems with substantial data transmission volumes they may not match the lifetime of LoRa devices. This positions LoRa as the preferred option for IoT applications where power efficiency plays a pivotal role.
LoRa uses small data packets at relatively low speeds, ranging from 300 bps to 37.5 kbps. Consequently, it finds more prevalent use in networks where high connection speeds are not a primary requirement.
In contrast, Zigbee provides higher data rates, ranging from 20 kbps to 250 kbps. This makes the protocol perfect for networks demanding real-time communication or frequent data exchange, such as those in home automation and industrial monitoring systems.
LoRa networks use point-to-point or star topologies, where gateways act as intermediaries, relaying messages between individual endpoints and a central network server.
Zigbee networks offer versatility by supporting various topologies, including mesh, tree, peer, and star configurations. This flexibility enhances scalability and lets devices communicate directly with each other or through intermediate nodes, resulting in the establishment of self-healing networks.

As LoRa can transmit data across extensive distances and penetrate walls and similar obstacles, LoRa systems require fewer gateways than Zigbee to accommodate an equivalent number of devices. This leads to a noteworthy reduction in network equipment costs. Moreover, the simplicity of installing and deploying LoRa devices compared to Zigbee further contributes to cost-effectiveness, making LoRa a more economically efficient solution.
What this LoRa vs Zigbee comparison makes clear, is that choosing between them boils down to what your IoT network needs. LoRa is a perfect choice for setups where you need to establish communication over long distances and keep power usage low, while Zigbee gives you more flexibility and scalability in terms of network structure, making it the go-to for setups that demand high throughput. Ultimately, making the right IoT choice depends on the specific requirements of your project.
Stay on top of the latest industry news
Thank you, we have received your message. Our manager will contact you shortly.
Our experts are always happy to help and promptly answer your questions. Please fill out the form to discuss your project and develop a tailored action plan.
Thank you, we have received your message. Our manager will contact you shortly.
Thank you, we have accepted your request. In the near future the responsible manager will contact you and clarify the details of the order.
Our experts are always happy to help and promptly answer your questions. Please fill out the form to discuss your project and develop a tailored action plan.
Thank you, we have received your message. Our manager will contact you shortly.